email protocols MAP and POP3 are two different email protocols. These protocols are used for retrieving emails from email servers. To simplify it, if you’re using an email client, you can configure the email client with either IMAP or POP3 to retrieve all your emails on a computer or any smart devices you own.
It’s up to you to decide whether you want to use IMAP or POP3. Below we’ve explained what each email protocol does and what the differences are between them.
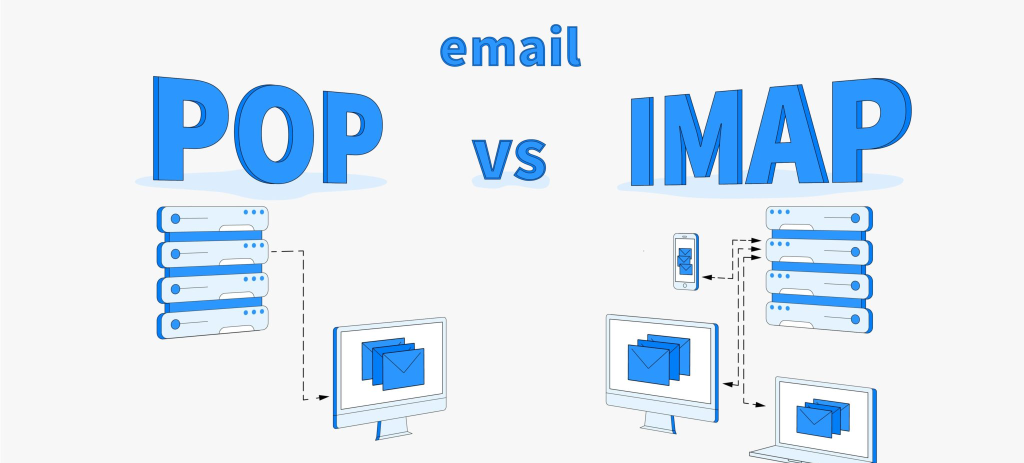
Email protocols What is POP3?
POP3 stands for post office protocol 3. One of the differences between IMAP and POP3 email protocols is that POP3 is simpler than IMAP. POP3’s only job is to download emails to your smart devices or computer from an email server. Additionally, POP3 only downloads emails that are in your inbox folder. For example, it will not download emails from your spam folder, your draft folder, your sent folder, your deleted emails, etc.
POP3 does not synchronise. This means that once POP3 email protocols retrieves emails from an email server, the email server will delete the emails. Therefore, there will be no saved copy on the email server once POP3 has retrieved it.
Thus, if you have two computers, once one of the computers retrieve your emails from the email server, the other computer will not be able to retrieve the emails as it’s already been deleted.
Benefits of POP3
POP3 uses bandwidth more efficiently than IMAP does. This is especially good if you have slow internet connections. There is no limitation on the size of your inbox with POP3.
What is IMAP?
IMAP stands for Internet message access protocol. IMAP allows you to view all your emails that’s on the email server from multiple devices. Not only are the emails saved on the email server, but IMAP also caches copies of your email to all your devices.
Additionally, IMAP synchronises all your folders. Unlike POP3, IMAP email protocols synchronises your inbox folder, sent folder, deleted folder etc.
When using IMAP, keep in mind that if you delete a retrieved email from your smartphone, that email will automatically be deleted from your computer and the email server. The same applies when you create a folder, the folder will also show up automatically on your computer and the email server.
Benefits of IMAP
- With IMAP, you can easily transfer all your old email archives to your new email program if you ever decide to switch email clients. It will only take a few minutes, and you can easily download all your emails from the server.
- When you choose an email set up with IMAP at one.com, all your emails will have a saved copy on the mail server. Meaning, if your computer breaks or gets stolen, you don’t have to worry about losing your data. Our backup system at one.com protects your mail against almost any risk you can imagine.
- Unlike POP3, IMAP saves a copy of your emails. Hence, IMAP can retrieve emails from the email server multiple times as a copy of the email will always exist on the server until you decide to delete it.
Difference between POP3 and IMAP protocol for mail
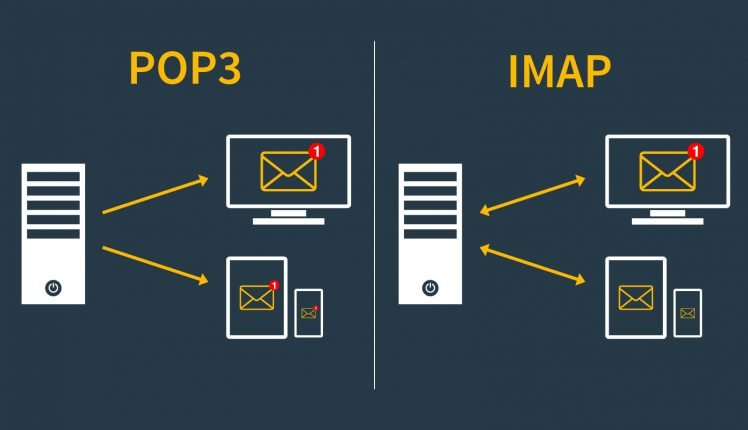
POP3 and IMAP – POP3 (Post Office Protocol) and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) are two commonly used email-protocols that allow users to access their email messages from a mail server.
Here are the key differences between POP3 and IMAP:
POP3 (Post Office Protocol):
- Download and Store:
- Behavior: POP3 is designed to download emails from the mail server to the user’s device.
- Storage: Emails are typically stored locally on the user’s device, and by default, they are removed from the server after downloading.
- Offline Access:
- Accessibility: Once emails are downloaded, they can be accessed even when the device is offline because the messages are stored locally.
- Single Device Synchronization:
- Usage: POP3 is traditionally used when users access their emails from a single device.
- Sync Behavior: Changes made on one device (such as marking an email as read) do not sync with other devices.
- Less Server Space Utilization:
- Storage Impact: Since emails are downloaded and removed from the server, POP3 generally consumes less server space compared to IMAP.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol):
- Store and Sync:
- Behavior: IMAP allows users to view and manipulate messages directly on the server without downloading them.
- Storage: Emails remain on the server, and changes made on one device (e.g., marking an email as read) are reflected on all devices connected to the same email account.
- Online Access:
- Accessibility: IMAP requires an internet connection to access emails since they are stored on the server.
- Multiple Device Synchronization:
- Usage: IMAP is suitable for users who access their email accounts from multiple devices (e.g., computer, smartphone, tablet).
- Sync Behavior: Changes made on one device are synchronized across all devices, providing a consistent view of the mailbox.
- More Server Space Utilization:
- Storage Impact: Since emails are stored on the server, IMAP can consume more server space compared to POP3, especially if users have a large volume of emails.
Which Protocol to Choose (choice between POP3 and IMAP):
- POP3: Suitable for users who primarily access emails from a single device and prefer to store emails locally. However, it may not be the best choice for those who need to access emails from multiple devices and want changes to be synchronized.
- IMAP: Ideal for users who access their emails from multiple devices and want changes (read/unread status, folders, etc.) to be synchronized across all devices. IMAP is commonly used in today’s interconnected and multi-device environments.
In summary, the choice between POP3 and IMAP depends on your specific needs, such as the number of devices you use to access email, the importance of synchronization, and your preferred approach to email storage.

